|
|
 Wind Wind
What is Wind?
 Wind is air in motion. It is produced by the uneven
heating of the earth’s surface by the sun. Since the earth’s surface
is made of various land and water formations, it absorbs the sun’s
radiation unevenly. Two factors are necessary to specify wind: speed and
direction. Wind is air in motion. It is produced by the uneven
heating of the earth’s surface by the sun. Since the earth’s surface
is made of various land and water formations, it absorbs the sun’s
radiation unevenly. Two factors are necessary to specify wind: speed and
direction.
What causes the wind to blow?
 As the sun warms the Earth's surface, the atmosphere warms
too. Some parts of the Earth receive direct rays from the sun all year and are
always warm. Other places receive indirect rays, so the climate is colder. Warm
air, which weighs less than cold air, rises. Then cool air moves in and
replaces the rising warm air. This movement of air is what makes the wind
blow. As the sun warms the Earth's surface, the atmosphere warms
too. Some parts of the Earth receive direct rays from the sun all year and are
always warm. Other places receive indirect rays, so the climate is colder. Warm
air, which weighs less than cold air, rises. Then cool air moves in and
replaces the rising warm air. This movement of air is what makes the wind
blow.
What is a derecho?
  A derecho is a widespread and long-lived windstorm that
is associated with a fast-moving band of severe thunderstorms. They can produce
significant damage to property and pose a serious threat life, primarily by
downburst winds. To be classified as a derecho, the path length of the storm
has to be at least 280 miles long. Widths may vary from 50-300 miles. Derechos
are usually not associated with a cold front, but a stationary front. They
occur mostly in July, but can occur at anytime during the spring and
summer. A derecho is a widespread and long-lived windstorm that
is associated with a fast-moving band of severe thunderstorms. They can produce
significant damage to property and pose a serious threat life, primarily by
downburst winds. To be classified as a derecho, the path length of the storm
has to be at least 280 miles long. Widths may vary from 50-300 miles. Derechos
are usually not associated with a cold front, but a stationary front. They
occur mostly in July, but can occur at anytime during the spring and
summer.
What is the jet stream?
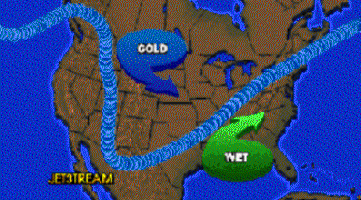 The jet stream is a fast
flowing, river of air found in the atmosphere at around 12 km above the surface
of the Earth just under the tropopause. The jet stream is a fast
flowing, river of air found in the atmosphere at around 12 km above the surface
of the Earth just under the tropopause.  They form at the boundaries of adjacent
air masses with significant differences in temperature, such as of the polar
region and the warmer air to the south. Because of the effect of the Earth's
rotation the streams flow west to east, propagating in a serpentine or
wave-like manner at lower speeds than that of the actual wind within the
flow. They form at the boundaries of adjacent
air masses with significant differences in temperature, such as of the polar
region and the warmer air to the south. Because of the effect of the Earth's
rotation the streams flow west to east, propagating in a serpentine or
wave-like manner at lower speeds than that of the actual wind within the
flow.
What are the global wind patterns?
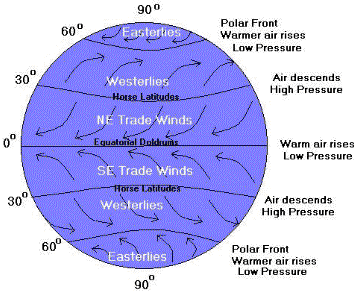 The equator receives the Sun's direct rays. Here, air is heated and rises, leaving
low pressure areas behind. Moving to about thirty degrees north and south of the equator, the warm air from the equator begins to cool and sink. Between
thirty degrees latitude and the equator, most of the cooling sinking air moves back to the equator. The rest of the air flows toward the
poles. The equator receives the Sun's direct rays. Here, air is heated and rises, leaving
low pressure areas behind. Moving to about thirty degrees north and south of the equator, the warm air from the equator begins to cool and sink. Between
thirty degrees latitude and the equator, most of the cooling sinking air moves back to the equator. The rest of the air flows toward the
poles.
What are the trade winds?
The trade winds are just air movements toward the equator.
They are warm, steady breezes that blow almost continuously. The Coriolis Effect makes the trade winds appear to be curving to the west, whether they are
traveling to the equator from the south or north.
How is wind helpful to Earth?
Wind is the fastest growing source of electricity in the
world. It's often one of the least expensive forms of renewable power
available. Some experts say it can sometimes be the cheapest form of any kind
of power. Generating power from the wind leaves no dangerous waste products
behind. Best of all, its supply is unlimited.
What is a land breeze?
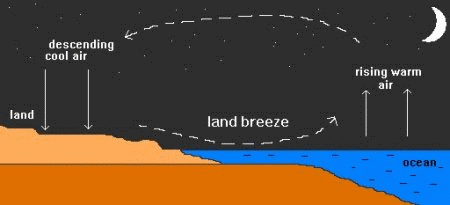 A land breeze occurs at night
when the land cools faster than the sea. In this case, it is air above the
warmer surface water that is heated and rises, pulling in air from the cooler
land surface. A land breeze occurs at night
when the land cools faster than the sea. In this case, it is air above the
warmer surface water that is heated and rises, pulling in air from the cooler
land surface.
What is a sea breeze?
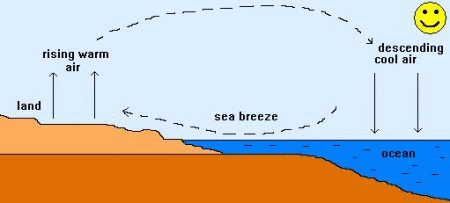 On a warm summer day along the coast, this differential
heating of land and sea leads to the development of local winds called sea
breezes. As air above the land surface is heated by radiation from the Sun, it
expands and begins to rise, being lighter than the surrounding air. To replace
the rising air, cooler air is drawn in from above the surface of the sea. This
is the sea breeze, and can offer a pleasant cooling influence on hot summer
afternoons. On a warm summer day along the coast, this differential
heating of land and sea leads to the development of local winds called sea
breezes. As air above the land surface is heated by radiation from the Sun, it
expands and begins to rise, being lighter than the surrounding air. To replace
the rising air, cooler air is drawn in from above the surface of the sea. This
is the sea breeze, and can offer a pleasant cooling influence on hot summer
afternoons.
How do windmills work?
 Windmills work because they slow down the speed of the
wind. The wind flows over the airfoil shaped blades causing lift, like the
effect on airplane wings, causing them to turn. The blades are connected to a
drive shaft that turns an electric generator to produce
electricity. Windmills work because they slow down the speed of the
wind. The wind flows over the airfoil shaped blades causing lift, like the
effect on airplane wings, causing them to turn. The blades are connected to a
drive shaft that turns an electric generator to produce
electricity.
What are some different types of wind
names?
Many local wind systems have
their own names. Here's a few!
chinook-(easterly off the Rocky
Mountains)
santa
ana-(easterly towards Southern California )
scirocco-(southerly
from North Africa to southern Europe)
mistral-(northwesterly from central France to
Mediterranean)
marin-(south-easterly from Mediterranean to France)
bora-(northeasterly from eastern
Europe to Italy)
gregale-(northeasterly from Greece)
etesian-(northwesterly from
Greece)
libeccio-(southwesterly
towards Italy)
|