|
|
 Hurricanes Hurricanes
What is a Hurricane?
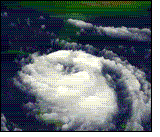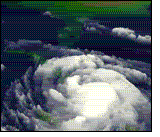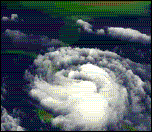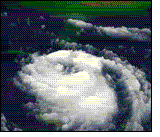
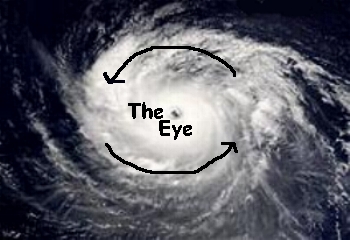 A hurricane is a
huge storm! It can be up to 600 miles across and have strong winds spiraling
inward and upward at speeds of 75 to 200 mph. Each hurricane usually lasts for
over a week, moving 10-20 miles per hour over the open ocean. Hurricanes gather
heat and energy through contact with warm ocean waters. Evaporation from the
seawater increases their power. Hurricanes rotate in a counter-clockwise
direction around an "eye." The center of the storm or "eye" is the calmest
part. It has only light winds and fair weather. When they come onto land, the
heavy rain, strong winds and large waves can damage buildings, trees and
cars.
A hurricane is a
huge storm! It can be up to 600 miles across and have strong winds spiraling
inward and upward at speeds of 75 to 200 mph. Each hurricane usually lasts for
over a week, moving 10-20 miles per hour over the open ocean. Hurricanes gather
heat and energy through contact with warm ocean waters. Evaporation from the
seawater increases their power. Hurricanes rotate in a counter-clockwise
direction around an "eye." The center of the storm or "eye" is the calmest
part. It has only light winds and fair weather. When they come onto land, the
heavy rain, strong winds and large waves can damage buildings, trees and
cars.
How do hurricanes form?
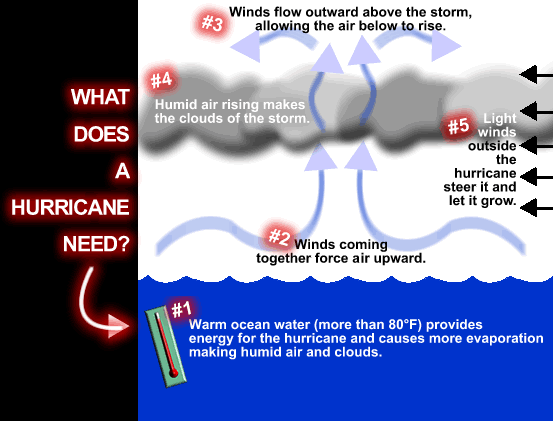 Hurricanes only form over really warm ocean water of
80°F or warmer. The atmosphere (the air) must cool off very quickly the
higher you go. Also, the wind must be blowing in the same direction and at the
same speed to force air upward from the ocean surface. Winds flow outward above
the storm allowing the air below to rise. Hurricanes typically form between 5
to 15 degrees latitude north and south of the equator. The
Coriolis Force is needed to create the spin
in the hurricane and it becomes too weak near the equator, so hurricanes can
never form there.
Hurricanes only form over really warm ocean water of
80°F or warmer. The atmosphere (the air) must cool off very quickly the
higher you go. Also, the wind must be blowing in the same direction and at the
same speed to force air upward from the ocean surface. Winds flow outward above
the storm allowing the air below to rise. Hurricanes typically form between 5
to 15 degrees latitude north and south of the equator. The
Coriolis Force is needed to create the spin
in the hurricane and it becomes too weak near the equator, so hurricanes can
never form there.
What is storm surge?
Storm surges are
frequently the most devastating element of a hurricane. As a hurricane’s
winds spiral around and around the storm, they push water into a mound at the
storm’s center. This mound of water becomes dangerous when the storm
reaches land because it causes flooding along the coast. The water piles up,
unable to escape anywhere but on land as the storm carries it landward. A
hurricane will cause more storm surge in areas where the ocean floor slopes
gradually. This causes major flooding. As
you watch the storm-surge animations, notice the effect that the physical
geography of each coastline has on storm surge. Also, note the waves on top of
the ocean's surface. Wind, waves, and sea-level rise all contribute to
storm-surge damage.
| Shallow-Water
Coastline |
 |
| Deep-Water
Coastline |
 |
With technology the way it is, there are computer models
that allow forecasters to predict the amount of storm surge that will affect a
coastal area. These are called Slosh Models and take into account a
storm’s strength, its path, how the ocean shallows, and the shape of the
land. Then it calculates how much storm surge a hurricane will probably
cause.
When does hurricane season start?
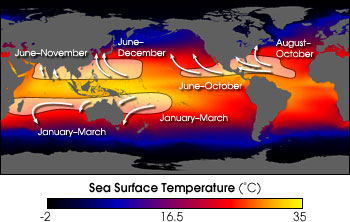 The Atlantic hurricane season
is from June 1 to November 30, but most hurricanes occur during the fall
months. The Eastern Pacific hurricane season is from May 15 to November 30.
(Below is a graphic that shows you when hurricanes are most active across parts
of the world.)
The Atlantic hurricane season
is from June 1 to November 30, but most hurricanes occur during the fall
months. The Eastern Pacific hurricane season is from May 15 to November 30.
(Below is a graphic that shows you when hurricanes are most active across parts
of the world.)
Who names hurricanes?
From 1950 to 1952, tropical
cyclones of the North Atlantic Ocean were identified by the phonetic alphabet
(Able-Baker-Charlie-etc.), but in 1953 the US Weather Bureau switched to
women's names. The rest of the world eventually caught on, and naming rights
now go by the World Meteorological Organization, which uses different sets of
names depending on the part of the world the storm is in. Around the U.S., only
women's names were used until 1979, when it was decided that they should
alternate a list that included men's names too. There's 6 different name lists
that alternate each year. If a hurricane does significant damage, its name is
retired and replaced with another.
What is the difference between a hurricane and a typhoon?
Nothing except geography. Tropical storms occur in several
of the world's oceans, and except for their names, they are essentially the
same type of storm. In the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Eastern
Pacific Ocean, they are called hurricanes. In the Western Pacific Ocean, they
are called typhoons. In the Indian Ocean, the Bay of Bengal, and Australia,
these types of storms are called cyclones.
|
|